Ways in which investment companies can magnify income and capital returns, but which can also magnify losses.
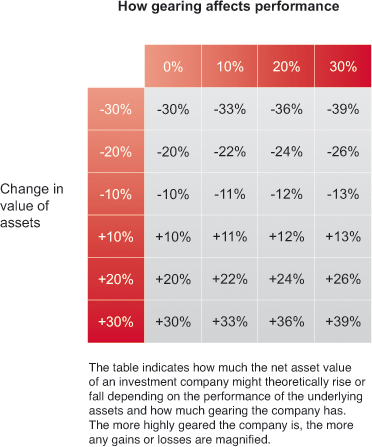
At its simplest, gearing means borrowing money to buy more assets in the hope the company makes enough profit to pay back the debt and interest and leave something extra for shareholders.

However, if the investment portfolio doesn’t perform well, gearing can increase losses. The more an investment company gears, the higher the risk.
Investment companies can usually borrow at lower rates of interest than you’d get as an individual. They also have flexible ways to borrow – for example they might get an ordinary bank loan or, for split capital investment companies, issue different classes of share.
Not all investment companies use gearing, and most use relatively low levels of gearing.



 Data provided by Morningstar.
Data provided by Morningstar.
 Company documents provided by FE fundinfo.
Company documents provided by FE fundinfo.